Outsourcing has long been a strategic tool for companies seeking to balance innovation with efficiency. It allows organizations to cut development costs, scale with specialized expertise, and speed up time-to-market. This is especially true in information technology—the most outsourced industry worldwide—where agility and technical excellence often give a competitive edge. Industry data highlights the prevalence and benefits of IT outsourcing services:
- 37% of IT operations are entrusted to third-party vendors.
- 64% of outsourced services worldwide are accounted for by software development.
- 76% of executives participating in Deloitte’s latest outsourcing survey claimed that their IT services were delivered via third-party models.
- 57% of IT businesses consider cost-cutting the primary driver for outsourcing.
Comparing outsourcing models
Outsourcing isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Different approaches meet specific business goals, such as closing skill gaps or delivering complex projects end-to-end. The two most common strategies are:
- Staff augmentation: A flexible model where external specialists integrate into in-house teams and processes to boost capacity or add expertise.
- Project-based outsourcing: An approach where an external partner manages the entire process of planning, execution, and delivery for a specific project.
While both approaches sit under the outsourcing umbrella, they shape very different relationships between client and vendor—impacting cost, flexibility, and speed.
In this guide, we’ll compare staff augmentation vs outsourcing, explore the best opportunities for each one, and discuss what factors to consider when choosing the right fit for your business goals.
What is staff augmentation?
Staff augmentation is an outsourcing strategy that lets companies quickly scale their teams by bringing in external specialists. When choosing staff augmentation, companies keep control of core management and processes in-house while filling skill or capacity gaps for short- or long-term needs.
With the U.S. market alone accounting for over $200 billion in the global staffing industry and 34% of U.S. workers freelancing, this model has become a core workforce strategy, giving businesses flexibility, scalability, and access to global talent without the commitments of permanent hiring.
How staff augmentation works
At its core, staff augmentation is about extending the capacity of your in-house team without significantly changing the way you run projects. The process usually starts with identifying gaps—whether you need an additional front-end developer for a new feature, QA engineers to expand testing coverage, or a designer to guide a new product. Instead of running a lengthy recruitment process, companies work with a vendor who already has a pool of vetted professionals. These specialists are then onboarded into your team and work under your direction, following your tools, processes, and priorities.
This makes the model highly flexible. You can scale up with five developers for a high-pressure quarter and scale down once the workload stabilizes. You can also bring in niche expertise for a few months without long-term commitments. In staff-augmentation-based engagements, remote experts operate as an extension of your team rather than an independent unit, but you get a certain degree of autonomy with models like dedicated teams.
Advantages of staff augmentation
Companies often turn to staff augmentation for the same reasons: cost efficiency, flexibility, and access to talent. Some of the key benefits include:
- Lower costs. You reduce expenses tied to recruiting, onboarding, HR, and permanent overhead.
- Speed to execution. Instead of spending months hiring, you can integrate specialists within days or weeks.
- Access to global talent. Staff augmentation vendors tap into global talent, letting you find expertise regardless of location.
- Flexibility. Projects can scale up or down quickly and easily in response to changing business goals and market conditions.
- Control over delivery. Unlike fully outsourced projects, you maintain control over team composition, development processes, and daily activities.
For many companies, this combination makes staff augmentation an attractive middle ground: you maintain full control and project ownership while gaining the reach of global hiring.
Challenges to consider
While staff augmentation offers speed and flexibility, it also comes with some challenges that companies should be mindful of:
- Integration into the team. External professionals need to adapt to your company’s culture, product context, team dynamics, tools, and workflows. If not given time for onboarding, they may struggle to align with existing processes, which can decrease productivity in the short term.
- Maintaining consistent quality. Since augmented staff follow your direction and internal standards, the burden of quality control remains in-house. When leveraging staff augmentation, companies often benefit from investing in strong project management, performance monitoring, and solutions for providing feedback to ensure consistent quality..
- Knowledge transfer and retention. Effective documentation is crucial for seamless product knowledge sharing between in-house and external teams. This ensures that valuable insights are easily accessible and utilized by all contributors.
- Data security, compliance, and IP protection. For industries handling sensitive data, such as healthcare, government, or finance, strict protocols are necessary to ensure that external contractors do not access restricted parts of software systems. While vendors often incorporate these requirements into their collaboration models, ongoing effort from in-house project management and technical leadership is still crucial for effective coordination.
High-quality modern staff augmentation vendors mitigate these issues through granular reporting, assistance with onboarding, stringent data policies, and more. Nevertheless, companies leveraging staff augmentation services still need to be mindful of the possible limitations of this model.
Project-based outsourcing
Project-based outsourcing shifts ownership of an entire initiative to an external partner, who manages planning, execution, and delivery based on client requirements. The client defines the goals, scope, and budget, while the vendor brings expertise, delivery processes, and accountability for results. This model is best suited for well-defined, time-bound projects such as building a mobile app, launching an analytics dashboard, or developing a complete platform end-to-end.
Unlike staff augmentation, where companies retain direct control over remote teams, project-based outsourcing places responsibility for execution, timelines, and outcomes entirely in the vendor’s hands. The client’s role is limited to setting requirements and reviewing progress at agreed checkpoints, while the outsourcing partner delivers a complete solution. This approach allows organizations to reduce management overhead, control costs, and keep internal teams focused on core business priorities.
How project-based outsourcing works
The process typically starts with outlining project objectives, deliverables, and deadlines. Once a vendor is selected, the outsourcing partner assembles the team, designs the execution plan, and assumes full responsibility for development.
Communication with the client is maintained through a designated Product Owner or Project Manager, who receives progress updates at agreed intervals. At the end of the engagement, the vendor delivers the finished product according to the agreed specifications.
Advantages of project-based outsourcing
The main appeal of project-based outsourcing lies in the ability to hand over full responsibility for delivery while maintaining clarity around costs and outcomes. This model is particularly attractive for organizations that want predictable results without the overhead of managing a product development team. Some of the key benefits include:
- Minimal time commitment from the client. The vendor handles planning, staffing, and execution, freeing internal teams to focus on core business initiatives.
- Cost predictability. Contracts are usually milestone- or deliverable-based, providing clearer budget planning compared to ongoing resource costs.
- Access to specialized expertise. Vendors bring niche technical skills, domain knowledge, and established methodologies that accelerate project delivery.
- Shifted accountability. Responsibility for meeting deadlines and delivering outcomes lies with the vendor, reducing internal risk.
- Efficiency in execution. Experienced partners can often deliver software solutions faster and more effectively than building a team from scratch in-house.
Challenges to consider
While project-based outsourcing offers clear benefits, it also comes with potential risks that businesses should plan for:
- Limited flexibility. Because success depends on well-defined requirements, changes mid-project can lead to delays, added costs, or scope renegotiations.
- Reduced control. Delegating responsibility to an external partner means companies must rely on strong communication and governance to ensure quality.
- Vendor dependency. Outsourcing an entire project can create reliance on the partner for maintenance or future iterations if knowledge transfer is not carefully managed.
- Misaligned expectations. Without clear agreements, differences in delivery standards, timelines, or definitions of “done” can cause friction.
With the right safeguards — such as clear contracts, frequent updates, and strong project governance — these challenges can be mitigated, making project-based outsourcing an effective option for organizations seeking efficiency and predictability in delivery.
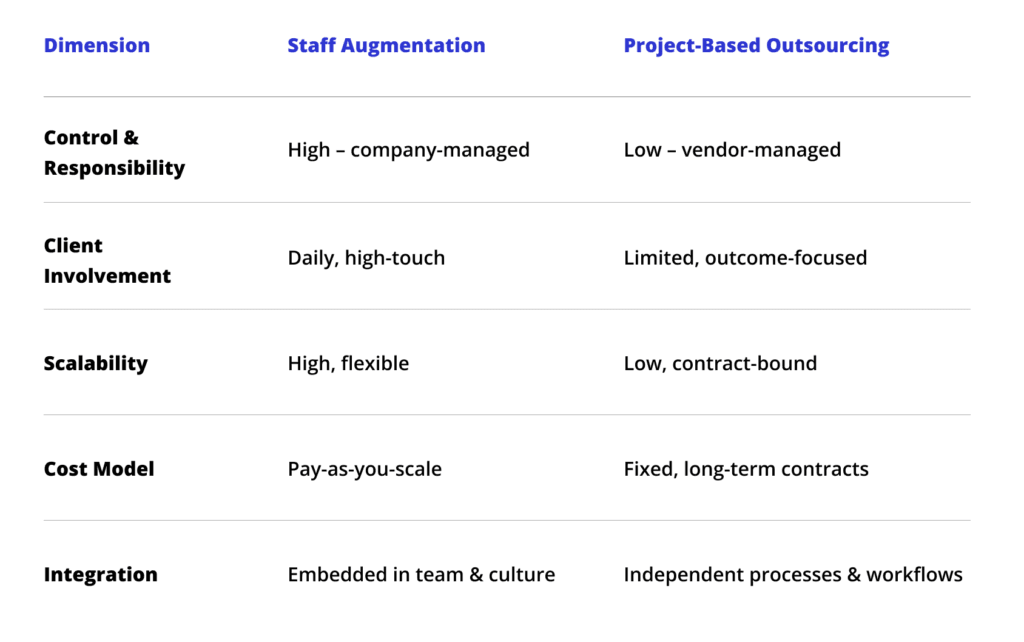
Staff augmentation vs. Project-based outsourcing
These differences in relationship shape how each model handles control, integration, cost, scalability, risk, and access to skills:
Control & responsibility
With most staff augmentation models, companies retain full ownership of workflows, task prioritization, and quality standards. External experts adapt to existing frameworks while leaving decision-making power in-house. In project-based outsourcing, the vendor typically assumes end-to-end responsibility for delivery. The client defines goals and outcomes, while the partner manages resources, quality, and reporting.
Team integration & culture fit
Augmented professionals embed directly into in-house teams, aligning with communication styles, tools, and project management practices. This creates minimal disruption to the company culture. Project-based vendors operate more independently, often bringing their own processes and tools. While this model can be highly efficient, cultural alignment and daily collaboration may be less seamless.
Cost models (short vs. long term)
Staff augmentation offers a flexible pay-as-you-scale approach that’s well-suited for short- and mid-term needs. Costs reflect actual resource usage without vendor overhead. Project-based outsourcing usually comes with structured contracts determining engagement duration, management layers, delivery guarantees, operational overhead, and more.
Scalability & flexibility
Staff augmentation allows resources to be added or released quickly in response to project demands, making it ideal for fluctuating workloads or pilot initiatives. Project-based outsourcing is better for stable, predictable workloads where changes are less frequent, but scaling typically requires renegotiating contracts.
Risk & security/IP
Strong Service Level Agreements (SLA) and governance frameworks are essential in both cases. Whether its staff augmentation or project-based outsourcing, companies need to conduct due diligence regarding vendors to ensure their security and IP protection policies align with their requirements.
Access to skills & innovation
Staff augmentation provides fast access to tech expertise without long recruitment cycles, which makes it optimal for filling skill gaps or accelerating delivery. Project-based outsourcing offers broader capabilities and full-spectrum delivery processes, though the pace of innovation depends on the vendor’s priorities.
Quick comparison at a glance
When to use staff augmentation and project-based outsourcing
Both staff augmentation and project-based outsourcing help companies bridge capability gaps, move faster, and optimize costs. But while they share some advantages, the right choice depends on how much control you want to keep and how much accountability you’re ready to transfer.
Shared advantages
No matter which approach you choose, both models offer:
- Access to expertise — quickly tap into specialized talent without lengthy recruitment.
- Faster execution — scale delivery capacity to meet deadlines or seize opportunities.
- Cost efficiency — outsourcing helps offset rising U.S. developer salaries by offering access to equally skilled talent in more cost-effective regions. See our 2025 Tech Salary Report for detailed comparisons.
- Flexibility — adjust your resourcing as priorities and workloads evolve.
- Reduced hiring burden — skip the overhead of recruiting, onboarding, and retaining talent.
Both models make your organization more agile, but they shape very different working relationships. Here’s how to know which one fits your situation best:
When to choose staff augmentation
Best suited for situations where your team leads the development process, but needs reinforcement. Practical use cases include:
- Bridging skill gaps without forming a new team
Example: You need a cloud security specialist for a migration project but don’t want to recruit or train a full security team. - Maintaining established processes and culture
External specialists work under your workflows and standards, preserving consistency in methodologies like Agile, DevOps, or internal QA protocols. - Scaling capacity temporarily
Useful for seasonal spikes, product launches, or unexpected client wins where workload expands suddenly but won’t stay that way long term. - Handling sensitive projects
Because augmented staff integrate directly into your team, sensitive data, IP, or compliance-heavy tasks stay under your governance. - Trial-to-hire opportunities
Augmented engagements can evolve into long-term employment if both sides see a good fit.
When to choose project-based outsourcing
Best for cases where project delivery is more valuable than maintaining direct control. It works particularly well when:
- The project has a clear scope and outcome
Example: Developing a mobile app with defined features, timeline, and release milestones. - You have side projects that require dedicated resources
Outsourcing allows your employees to focus on core strategic work while the vendor drives the side initiative. - Specialized infrastructure or frameworks are needed
Vendors often bring established pipelines, tooling, and delivery models, reducing ramp-up time and technical overhead. - Predictable costs and deadlines are critical
Fixed contracts and service-level agreements make budgeting and accountability more straightforward. - Non-core projects need attention
Delegating maintenance, support, or backlog projects prevents them from stalling while internal resources stay aligned to business priorities.
Hybrid models: combining the best of both
In practice, many organizations don’t stick to a single model. Instead, they mix staff augmentation and project outsourcing to match the complexity of their portfolios. Common hybrid patterns include:
- Core innovation in-house, secondary work outsourced
Example: Augment your product team with AI/ML engineers while outsourcing routine QA and support. - Strategic projects outsourced, integration managed internally
The vendor delivers the full system, but your augmented staff ensures compatibility with legacy platforms and internal tools. - Parallel delivery streams
Staff augmentation accelerates ongoing development, while an outsourced vendor executes a time-boxed side project (e.g., building a client-facing portal).
Hybrid approaches help balance control, speed, and cost-efficiency. They’re particularly useful for companies scaling quickly, managing large portfolios, or handling both exploratory and operational projects at the same time.
Conclusion
Staff augmentation and project-based outsourcing aren’t competing solutions so much as complementary ones. Few organizations rely exclusively on a single model; most find themselves using both at different points, or blending them into a hybrid approach.
What matters most is clarity—knowing what your project demands, what your team can realistically deliver in-house, and where external support adds the most value. Framing the decision in those terms keeps the focus on outcomes, not on industry buzzwords or trends.
The strongest sourcing strategies are the ones that evolve with your business, adapting as priorities, capacity, and opportunities shift.













